5 Questions to tell you everything you need to know about Trauma
In the following article, I will cover the following 5 questions:
2. What are the different types of trauma?
3. How does trauma change a person?
4. Why would a person need a specialist to navigate through trauma?
What is Trauma?
Trauma is fear that is out of control. Fear, however, is a normal and NEEDED part of human life. Fear is really a set of chemical reactions in the brain that are set off to keep a person safe. For ![]() (I hate zombies) Fear will prompt you to do 1 of 3 things: You will either Fight, Freeze or Run
(I hate zombies) Fear will prompt you to do 1 of 3 things: You will either Fight, Freeze or Run 
… As a result, you will either get away, beat the zombie up or stay so still the zombie loses your scent. Either way, you will no longer have a reason to fear and your brain will give you permission to calm down. As a result, your fear responses have allowed living another day in a zombie infested world.
Jokes aside, problems happen when the brain does not give a person permission to calm down. Therefore, that person gets stuck in fear. This is trauma. As you will see below, trauma will change the function of the brain, belief system, and body. So, what are the types a trauma a person can experience?

4 Types of Trauma
1. Acute Trauma- A single traumatic event that lasts for a limited period of time. This is the instance where trauma is created by something so immense that the brain has a hard time processing the event.
Examples
Being in a car accident Seeing a loved one die A single physical or sexual assault Going through a natural disaster
2. Chronic Trauma- The experience of multiple traumatic events, often over a long period of time.
Examples
A child who On Monday sees a violent fight On Wednesday gets hurt in a drive-by shooting Then spends weeks in the hospital undergoing scary medical procedures.
3. Neglect- Failure of a caregiver to provide for the basic needs of someone who is unable to care for themselves. Of all the types of abuse (sexual, emotional, physical) neglect has
Please Note:
Neglect is perceived as trauma by infants and children.
It may reduce a child’s ability to recover from a trauma.
This abuse opens the door to other traumatic events.
4. Complex Trauma- When children are exposed to chronic trauma from the actions of parents or other adults who should have been caring for and protecting them.
Examples
Multiple traumatic events An abuse that began at a very young age The abuse caused by loved ones
Trauma will change the function of the brain, belief system, and body.
How does trauma change a person?
Trauma will physically change the brain.
The brain grows and functions on a use it or lose it principle. Meaning, the parts that are used the most is built up the most. For this reason, a child’s brain exposed to complex trauma would actually physically and behaviorally be different than another child that did not experience trauma. Parts of the brain (specifically towards the brain stem) will be larger than a non-traumatized brain.
Trauma changes the belief.
Out of control fears becomes irrational fears real quick. A person’s perceived happiness is 80% perception. If a traumatized person believes they are unsafe it trickles into every other part of daily functioning. Beliefs will impact thoughts, which impact emotions, which ultimately impact actions. For this person, trauma becomes a mental prison that limits that their potential.
Trauma changes your body.
Research is now backing up the fact that trauma affects eating, sleep, blood pressure, heart diseases, impulsiveness, autoimmune diseases. The hard fact is that the will body keep the score. Even when memory fails, the body often remembers. And it pays us back with disorders, diseases, and unexplainable pains.
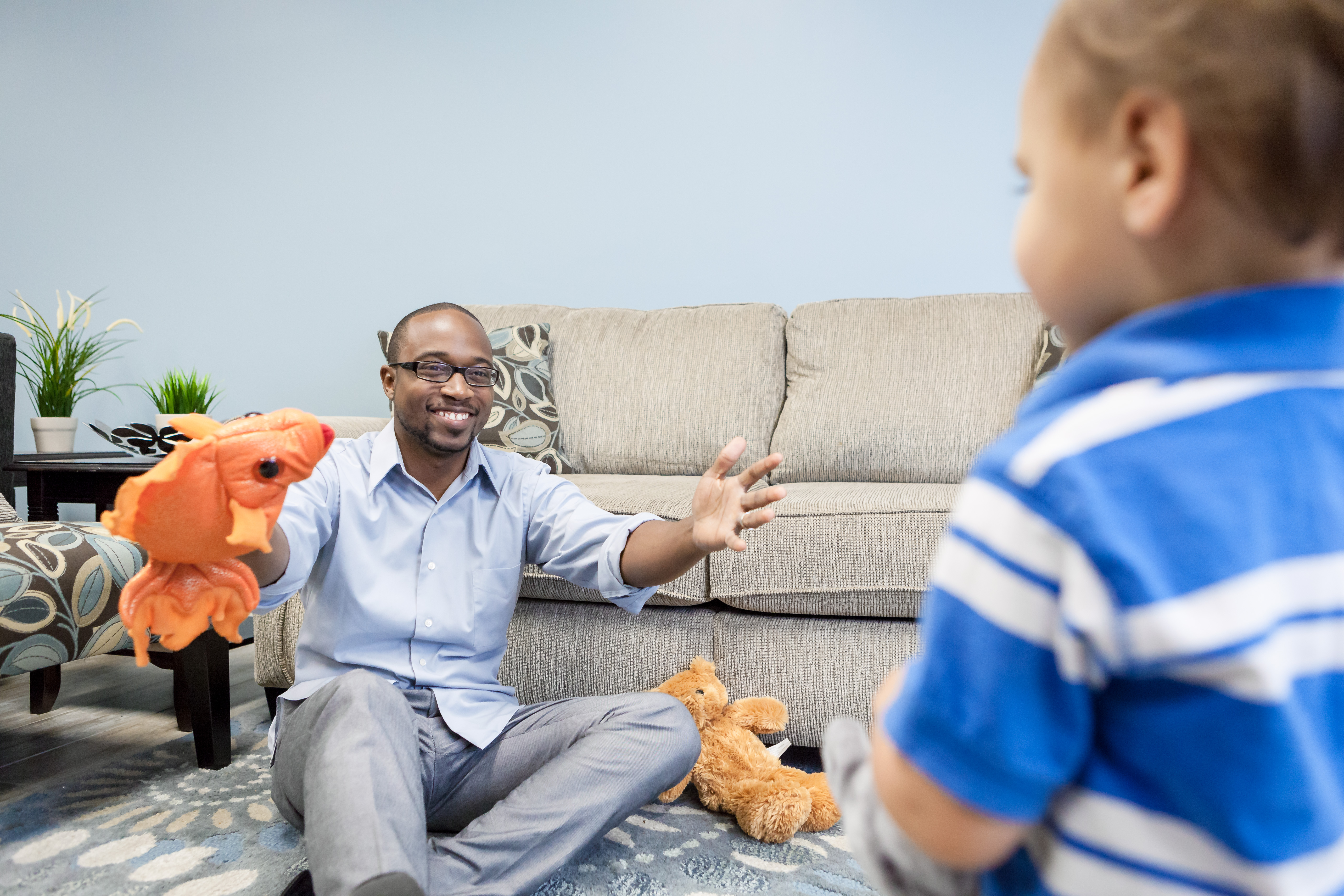

Why you need a specialist to navigate through trauma?
1.
It is dangerous work.
The therapist needs to understand that the core of the diagnosed problems is a person stuck in fear. The problem is not primarily behavioral. For that reason, if a therapist gives behavioral therapy without a trauma-informed lens their client can end up getting even more damaged.
2.
Trauma stands in the way of your best life.
Things will get stuck until trauma is dealt with.
Relationships = Stuck Health = Stuck Spiritual growth = Stuck Self-discipline = Stuck Insecurities = Stuck Identity = Stuck
When you can clear out the trauma, you can get free to work on all the other aspects of life without the weight of the past.
3.
It is hard work.
There is nothing pretty about healing trauma. It isn’t always fast, it isn’t always easy. In fact, for most, it gets worse before it gets better. But the effort alone will offer massive healing. Just trying to face the events that you have avoided produces resilience. Working on resolving trauma is one of those things you just have to take a risk to do, find a therapist you can trust.
The BEST 3 trauma therapies for all age groups?
Trauma Therapy for 0-5 years old
Child-Parent Psychotherapy (CPP)

What is it?
What does a CPP session look like?
How long does CPP take?
Pros and Cons
- One of the few empirically based treatment models for children under 6 years old
Cons
- This treatment takes a long time compared to other models
Links
Trauma Therapy for 3-5 years old
Trauma-Focused Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (TFCBT)

What is it?
What does a TFCBT session look like?
What is an TFCBT therapy session like?
Pros and Cons
- Flexible model
- Provides a clear map of the direction of therapy
Cons
- Focus on talk therapy, what is not always ideal in working with children
Links
Trauma work for 5-years-old – Adult
Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR)

What is it?
What does a EMDR session look like?
How long does EMDR take?
Pros and Cons
- Offers faster relief than other therapy models.
- There is no need to “talk” about past trauma.
Cons
- Fairly new therapy modality
Links
Links
http://www.cebc4cw.org/program/eye-movement-desensitization-and-reprocessing/ http://www.cebc4cw.org/program/eye-movement-desensitization-and-reprocessing/ https://www.emdria.org/page/emdr_therapy